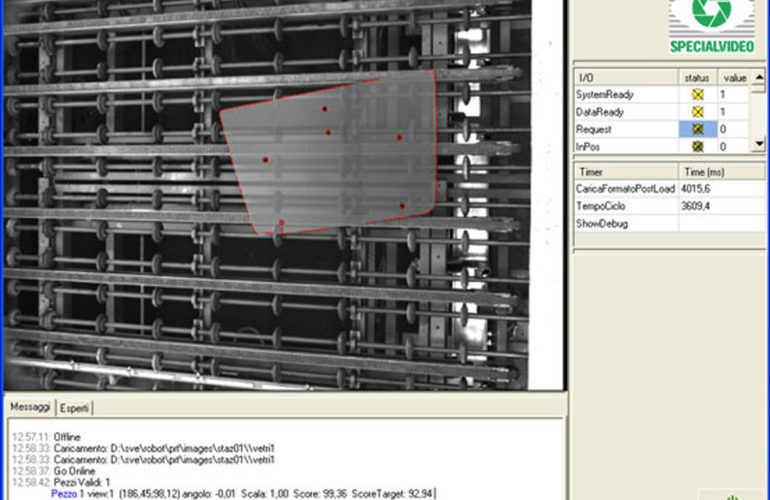
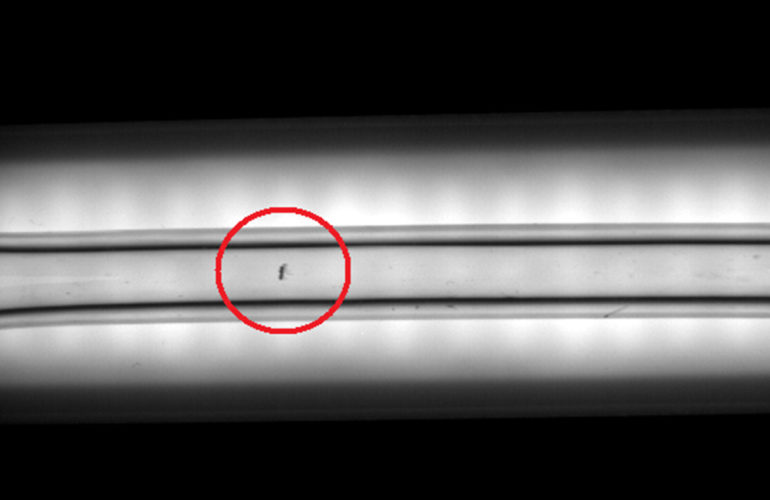
System Features
The main measurement system characteristic is obviously its accuracy. In machine vision systems the measurements accuracy depends primarily on the object size or the particular to measure, or by the camera captured area .
With stationary objects is possible to achieve accuracies of 1/10 of pixels (equivalent to microns for objects up to 10mm).The measurements can also be done during on-line processes and with moving objects. In this case 1/2 pixels accuracies can be reached .
The other factors that affect the accuracy of the measurements are manifold: from electrical noise (ripple power, electrical noise, jitter) problems related to non “ideal” illuminator (stability, uniformity) and objectives (perspective deformations).
To limit these factors, SPECIALVIDEO puts to fruit the specific experience gained in the field of computer vision, the choice of components and the implementation of special software algorithms to compensate for the unavoidable residual errors (due to non-ideal components).
The production line checks allow you to discard the out of tolerance products and can prevent the creation of defective parts, noting in advance a slow degeneration of the production process, and allowing you to focus on causes that undermine the quality of the product.
Benefits
Some of the major vision benefits in the measuring systems field are:
Label and spout position measurement
The function of this system is to measure the correct position of the label and of the spout with respect to the bottle.
The spout position measurement allows to discard the bottles with defective closure that would ultimately damage an entire carton of product.
The system is positioned downstream from the labeling machine, and by using two cameras controls the bottle sides on which the labels are applied.
The lighting was designed to highlight the label with respect to the bottle which normally has a very similar color. There are developed special compensation algorithms to eliminate the errors introduced by the pieces rotation with respect to the vertical axis.
Windshield base position measurement
The purpose of the system is to control the windshield immediately after bonding the base support of the back mirror viewer.
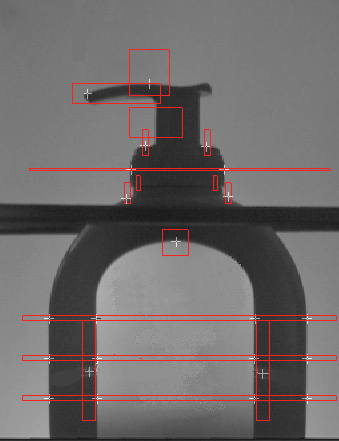
The vision system is constituted by a monochromatic matrix camera which frames the base, illuminated by a lighting tailormade device.
The functions carried out are the following: measure of the distance from the base edge of the glass, unit inclination calculation, position check in relation to any screen printing, the base presence select.
The data from vision system are used for statistical analysis, such as trend or cards XR, and documentation of test results.
"Measured" for the customer
The system is “custom” designed and implemented with regard to:
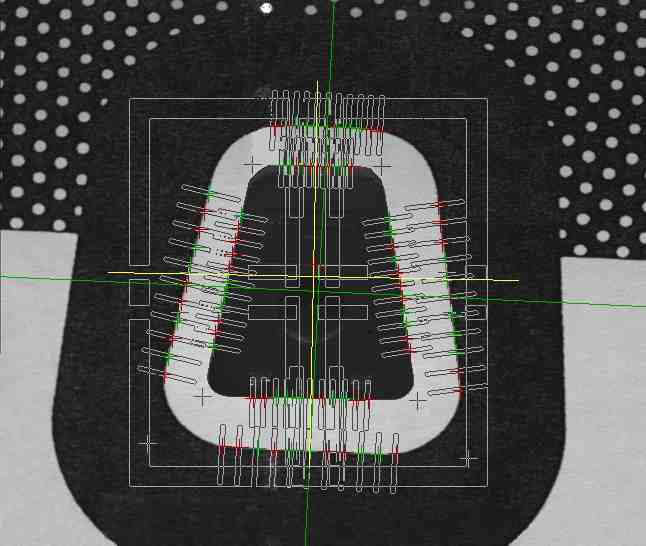
Precision Measurements
The dimensional object measurement by its image may at first seem equivalent to count the pixels number assigned to the object. In case of precision measurements is not like this because: The object edges are usually blurred, ie they involve several pixels (from 2to 5,normally ), then there is no point in the “real” board image. Determine the border point by a threshold binarization constrains the enlightenment system stability, because the measurement has to depend on the illuminationlevel (a dark object in bright field gets smaller increasing the light background) If the distance is variable, equally variable is the measure.
The techniques to obtain independent illumination level measurements uses the derivative analysis, similarly, the transformations produced by appropriate filters. In other words,in the picture we are looking for the more plausible place object to background transition, using all the pixels involved in the transition. The next important step is the measurement conversion from pixels to millimeters or, more generally, from the camera reference system to the space one in which the object is located. In both cases, the usual way to calculate the from pixels to millimeters is through a calibration function it can be found those parameters (for example, the scale factor) that transform “the best” measures from pixels to millimeters.